Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.

Synergistic role of nucleotides and lipids for the self-assembly of Shs1 septin oligomers
Amira capacities for membranes and filaments segmentation in cryo-TEM images are featured on the front cover of Biochemical Journal, July 2020.
Budding yeast septins are essential for cell division and polarity. (…) [The authors] have dissected, here, for the first time, the behavior of the Shs1 protomer bound to membranes at nanometer resolution, in complex with the other septins. Using electron microscopy, [the authors] have shown that on membranes, Shs1 protomers self-assembl... Read more
Cyntia Taveneau, Rémi Blanc, Gerard Pehau-Arnaudet, Aurélie Cicco, Aurélie Bertin

The molecular basis for sarcomere organization in vertebrate skeletal muscle
Sarcomeres are force-generating and load-bearing devices of muscles. A precise molecular picture of how sarcomeres are built underpins understanding their role in health and disease. Here, we determine the molecular architecture of native vertebrate skeletal sarcomeres by electron cryo-tomography.
Our reconstruction reveals molecular details of the three-dimensional organization and interaction of actin and myosin in the A-band, I-band, and Z-disc and demonstrates that α-actinin cros... Read more
Zhexin Wang, Michael Grange, Thorsten Wagner, Ay Lin Kho, Mathias Gautel, Stefan Raunser
The Architecture of Traveling Actin Waves Revealed by Cryo-Electron Tomography
Actin waves are dynamic supramolecular structures involved in cell migration, cytokinesis, adhesion, and neurogenesis. Although wave-like propagation of actin networks is a widespread phenomenon, the actin architecture underlying wave propagation remained unknown. In situ cryo-electron tomography of Dictyostelium cells unveils the wave architecture and provides evidence for wave progression by de novo actin nucleation. Subtomogram averaging reveals the structu... Read more
Marion Jasnin, Florian Beck, Mary Ecke, Yoshiyuki Fukuda, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Wolfgang Baumeister, Günther Gerisch
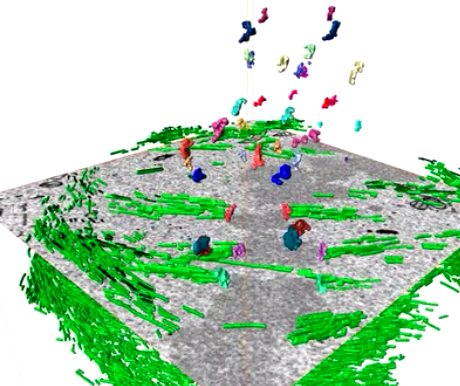
Serial block face scanning electron microscopy (SBF-SEM) is a powerful method to analyze cells in 3D. Here, working at the resolution limit of the method, we describe a correlative light–SBF-SEM workflow to resolve microtubules of the mitotic spindle in human cells. We present four examples of uses for this workflow that are not practical by light microscopy and/or transmission electron microscopy. First, distinguishing closely associated microtubules within K-fibers; second, resolving brid... Read more
Faye M. Nixon, Thomas R. Honnor, Nicholas I. Clarke, Georgina P. Starling, Alison J. Beckett, Adam M. Johansen, Julia A. Brettschneider, Ian A. Prior, Stephen J. Royle
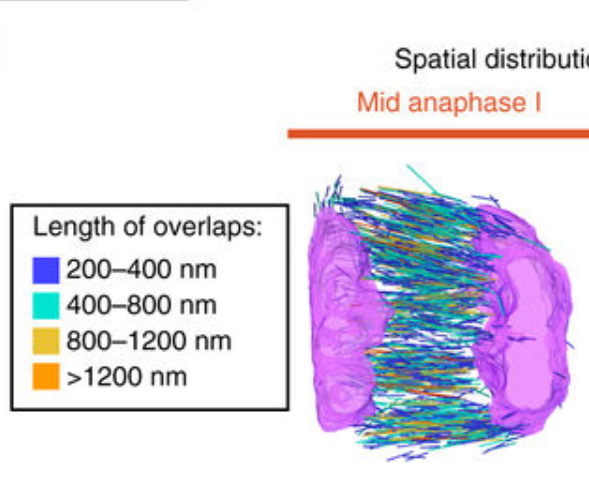
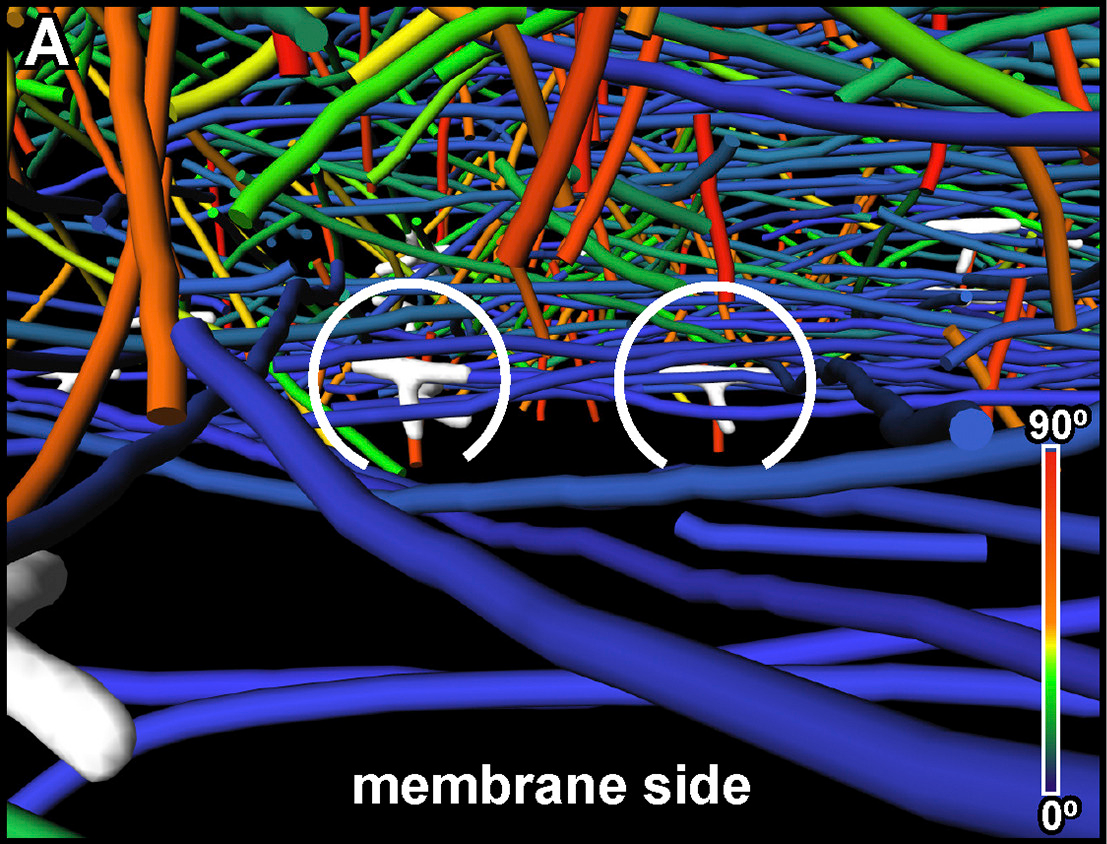
Chromosome segregation occurs by microtubule pushing in oocytes
During cell division, spindle microtubules ensure an equal repartition of chromosomes between the two daughter cells. While the kinetochore-dependent mechanisms that drive mitotic chromosome segregation are well understood, in oocytes of most species atypical spindles assembled in absence of centrosomes entail poorly understood mechanisms of chromosome segregation. In particular, the structure(s) responsible for force generation during meiotic chromosome separation in oocytes is unclear. Usin... Read more
Kimberley Laband, Rémi Le Borgne, Frances Edwards, Marine Stefanutti, Julie C. Canman, Jean-Marc Verbavatz, Julien Dumont
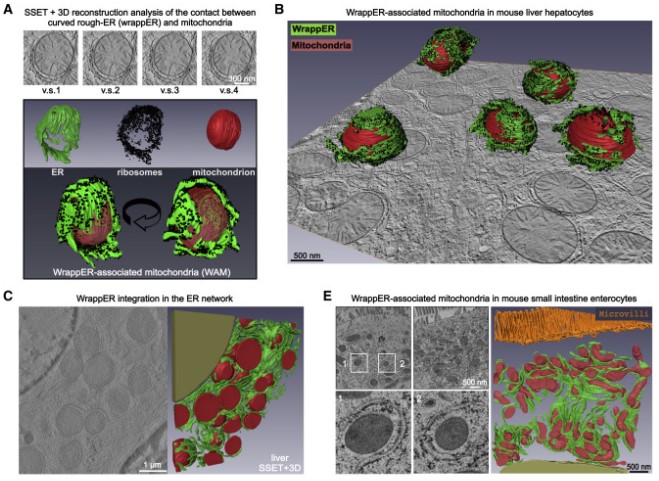
Mitochondria-rough-ER contacts in the liver regulate systemic lipid homeostasis
In this work, we studied mitochondria-rER contacts in vivo by serial section electron tomography (SSET) and 3D reconstruction analysis of cryo-fixed mouse tissue samples. We characterized this inter-organelle association as mitochondria tightly wrapped by sheets of curved rER (wrappER). Further, we used multi-omics and genetic approaches to obtain evidence that the wrappER is a distinct intracellular compartment and demonstrate the importance of wrappER-mitochondria contacts for v... Read more
Irene Anastasia, Nicolò Ilacqua, Andrea Raimondi, Philippe Lemieux, Rana Ghandehari-Alavijeh, Guilhem Faure, Sergei L. Mekhedov, Kevin J. Williams, Federico Caicci, Giorgio Valle, Marta Giacomello, Ariel D. Quiroga, Richard Lehner, Michael J. Miksis, Katalin Toth, Thomas Q. de Aguiar Vallim, Eugene V. Koonin, Luca Scorrano, Luca Pellegrini
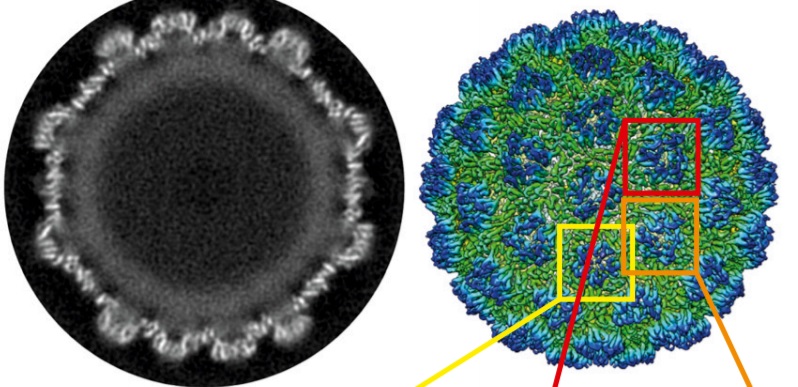
Structure of the Ty3/Gypsy retrotransposon capsid and the evolution of retroviruses
Retroviruses evolved from long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons by acquisition of envelope functions, and subsequently reinvaded host genomes. Together, endogenous retroviruses and LTR retrotransposons represent major components of animal, plant, and fungal genomes. Sequences from these elements have been exapted to perform essential host functions, including placental development, synaptic communication, and transcriptional regulation. They encode a Gag polypeptide, the capsid domains ... Read more
Svetlana O. Dodonova, Simone Prinz, Virginia Bilanchone, Suzanne Sandmeyer, and John A. G. Briggs
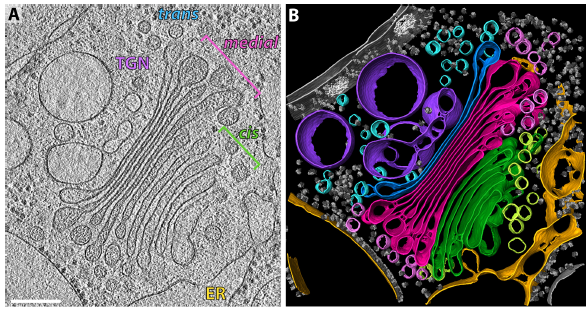
The structure of the COPI coat determined within the cell
COPI-coated vesicles mediate trafficking within the Golgi apparatus and from the Golgi to the endoplasmic reticulum. Here, we applied cryo-focused ion beam milling, cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram averaging to determine the native structure of the COPI coat within vitrified Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. The native algal structure resembles the in vitro mammalian structure, but additionally reveals cargo bound beneath beta’–COP. We find that all coat components disassemble... Read more
Yury S Bykov, Miroslava Schaffer, Svetlana O Dodonova, Sahradha Albert, Jurgen M Plitzko, Wolfgang Baumeister, Benjamin D Engel, John AG Briggs
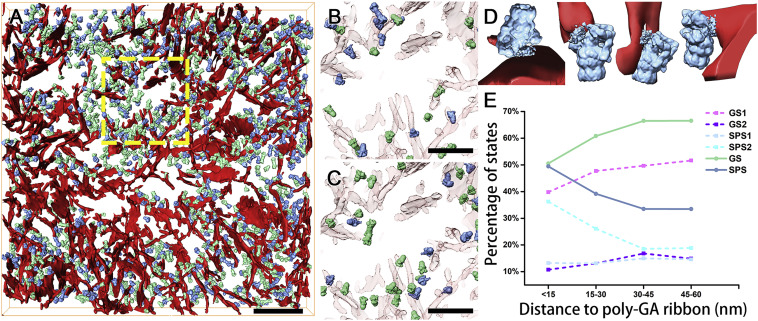
In Situ Structure of Neuronal C9orf72 Poly-GA Aggregates Reveals Proteasome Recruitment
Protein aggregation and dysfunction of the ubiquitin-proteasome system are hallmarks of many neurodegenerative diseases. Here, we address the elusive link between these phenomena by employing cryo-electron tomography to dissect the molecular architecture of protein aggregates within intact neurons at high resolution. We focus on the poly-Gly-Ala (poly-GA) aggregates resulting from aberrant translation of an expanded GGGGCC repeat in C9orf72, the most common genetic cause of amyotrophic latera... Read more
Qiang Guo, Carina Lehmer, Antonio Martinez-Sanchez, Till Rudack, Florian Beck, Hannelore Hartmann, Manuela Perez-Berlanga, Frederic Frottin, Mark S.Hipp, F. Ulrich Hartl, Dieter Edbauer, Wolfgang Baumeister, Ruben Fernandez-Busnadiego
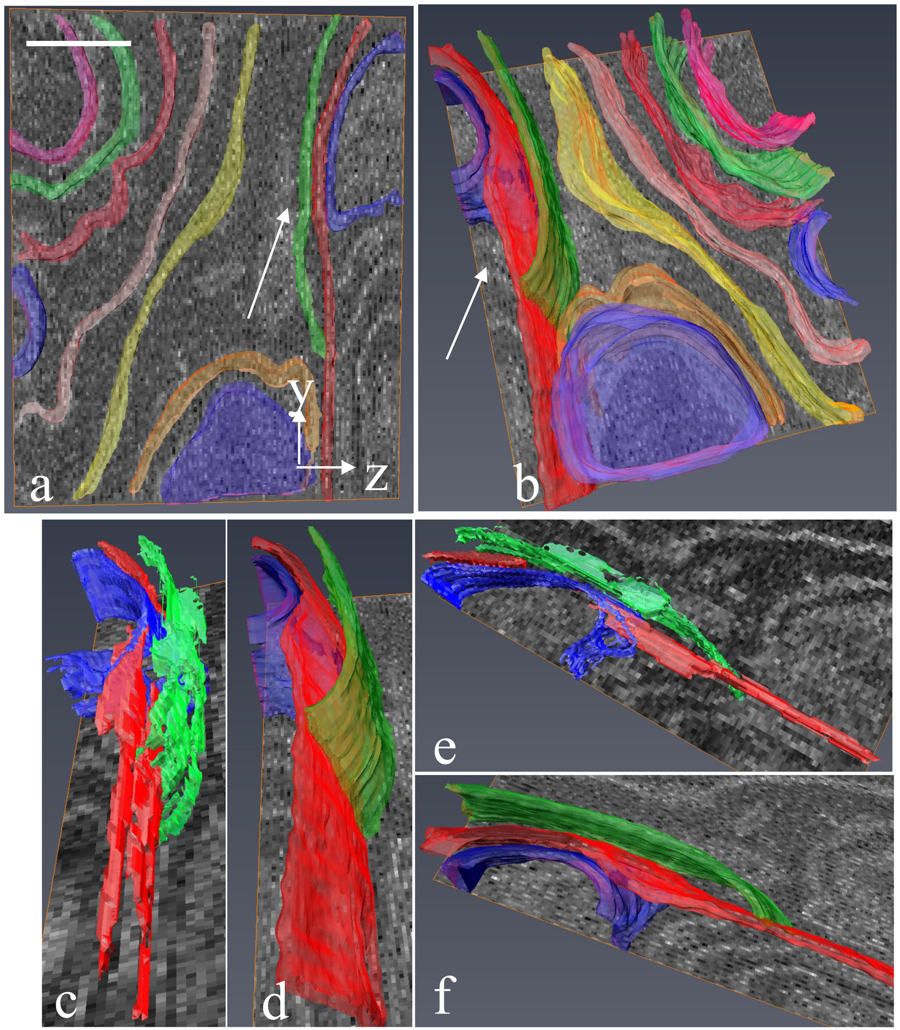
Serial block-face electron microscopy (SBEM) provides nanoscale 3D ultrastructure of embedded and stained cells and tissues in volumes of up to 107 µm3. In SBEM, electrons with 1–3 keV energies are incident on a specimen block, from which backscattered electron (BSE) images are collected with x, y resolution of 5–10 nm in the block-face plane, and successive layers are removed by an in situ ultramicrotome. Sp... Read more
Q. He, M. Hsueh, G. Zhang, D. C. Joy & R. D. Leapman
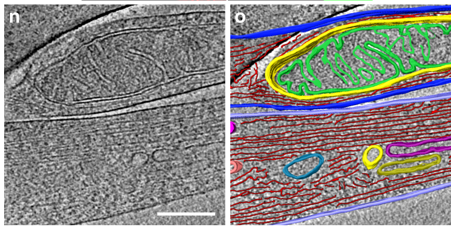
Correlative cryo-electron microscopy reveals the structure of TNTs in neuronal cells
The orchestration of intercellular communication is essential for multicellular organisms. One mechanism by which cells communicate is through long, actin-rich membranous protrusions called tunneling nanotubes (TNTs), which allow the intercellular transport of various cargoes, between the cytoplasm of distant cells in vitro and in vivo. Here, we use correlative FIB-SEM, light- and cryo-electron microscopy approaches to elucidate the structural organization of neuronal TNTs. Our data indicate ... Read more
Anna Sartori-Rupp, Diégo Cordero Cervantes, Anna Pepe, Karine Gousset, Elise Delage, Simon Corroyer-Dulmont, Christine Schmitt, Jacomina Krijnse-Locker & Chiara Zurzolo
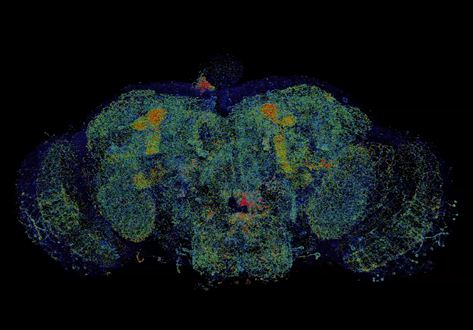
Combined expansion and lattice light sheet microscopy enables high
speed, nanoscale molecular imaging of neural circuits over large volumes.
Optical and electron microscopy have made tremendous inroads in understanding the complexity of the brain, but the former offers insufficient resolution to reveal subcellular details and the latter lacks the throughput and molecular contrast to visualize specific molecular constituents over mm-scale or larger dimensions. We combined expansio... Read more
Ruixuan Gao, Shoh M Asano, Srigokul Upadhyayula, Igor Pisarev, Daniel E Milkie, Tsung-Li Liu, Ved Singh, Austin Graves, Grace H Huynh, Yongxin Zhao, John Bogovic, Jennifer Colonell, Carolyn M Ott, Christopher Zugates, Susan Tappan, Alfredo Rodriguez, Kishore R Mosaliganti, Sean G Megason, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz, Adam Hantman, Gerald M Rubin, Tom Kirchhausen, Stephan Saalfeld, Yoshinori Aso, Edward S Boyden, Eric Betzig
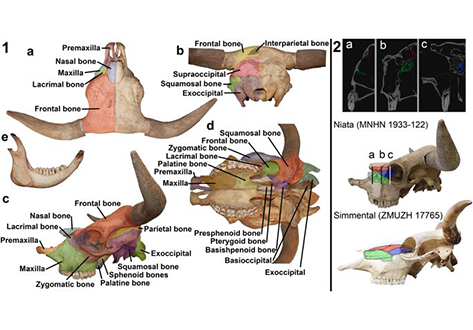
The Niata was a cattle variety from South America that figured prominently in writings on evolution by Charles Darwin. Its shortened head and other aspects of its unusual morphology have been subject of unsettled discussions since Darwin’s time. Here, we examine the anatomy, cranial shape, skull biomechanics, and population genetics of the Niata. Our results show that the Niata was a viable variety of cattle and exhibited anatomical differences to known chondrodysplastic forms. In cranial s... Read more
Kristof Veitschegger, Laura A. B. Wilson, Beatrice Nussberger, Glauco Camenisch, Lukas F. Keller, Stephen Wroe, Marcelo R. Sánchez-Villagra